Of Gurdjieff’s early life we know only what he has revealed in the autobiographical portions of his own writings, mainly Meetings with Remarkable Men. Although there is no reason to doubt the accuracy of his account, the fact remains that the principal aim of Gurdjieff’s writings was not to provide historical information but to serve as a call to awakening and as a continuing source of guidance for the inner search that is the raison d’être of his teaching. Pending further discussion of the nature of this search, we can say only that his writings are cast in forms that are directed not only to the intellectual function but also to the emotional and even subconscious sensitivities that, all together, make up the whole of the human psyche. His writings therefore demand and support the search for a finer quality of self-attention on the part of the reader, failing which the thought contained in them is unverifiable at its deeper levels.
Gurdjieff was born probably in 1866 of a Greek father and an Armenian mother in Alexandropol (now Gumri), Armenia, a region where Eastern and Western cultures mixed and often clashed. The environment of his childhood and early adolescence, while suggesting a near-biblical patriarchal culture, is also marked by elements not usually associated with these cultural traditions. The portrait Gurdjieff draws of his father, a well-known ashokh, or bard, suggests some form of participation in an oral tradition stretching back to mankind’s distant past. At the same time, Gurdjieff speaks of having been exposed to all the forms of modern knowledge, especially experimental science, which he explored with an impassioned diligence. The influence of his father and certain of his early teachers contrasts very sharply with the forces of modernity that he experienced as a child. This contrast, however, is not easily describable. The difference is not simply that of ancient versus modern worldviews or patterns of behavior, though it certainly includes that. The impression, rather, is that these “remarkable men” of his early years manifested a certain quality of personal presence or being. That the vital difference between human beings is a matter of their level of being became one of the fundamental elements in Gurdjieff’s teaching and is not reducible to conventional psychological, behavioral, or cultural typologies.
Meetings with Remarkable Men shows us the youthful Gurdjieff journeying to monasteries and schools of awakening in remote parts of Central Asia and the Middle East, searching for knowledge about man that neither traditional religion nor modern science by itself could offer him. The clues to what Gurdjieff actually found on these journeys are subtly distributed throughout the narrative, rather than laid out in doctrinal form. Discursive statements of ideas are relatively rare in the book, and where they are given it is with a deceptive simplicity that serves to turn the reader back to the teachings woven in the narrative portions of the text. Repeated readings of Meetings with Remarkable Men yield the realization that Gurdjieff meant to draw our attention to the search itself and that what he intended to bring to the West was not only a new statement of what has been called “the primordial tradition,” but the knowledge of how modern man might conduct his own search within the conditions of twentieth-century life. For Gurdjieff, as we shall see, the search itself, when rightly conducted, emerges as the principal spiritualizing force in human life, what one observer has termed “a transforming search,” rather than “a search for transformation.”1
Gurdjieff began his work as a teacher in Russia around 1912, on the eve of the civil war that led to the Russian Revolution. In 1914 he was joined by the philosopher P. D. Ouspensky and soon after by the well-known Russian composer Thomas de Hartmann. Ouspensky was later to produce In Search of the Miraculous, by far the best account of Gurdjieff’s teaching written by a pupil or anyone other than Gurdjieff, while de Hartmann, working in a unique collaboration with Gurdjieff, would produce what has come to be called the “Gurdjieff / de Hartmann music,” the qualities of which will be discussed below. Soon after, as the Revolution drew near and the coming breakdown of civil order began to announce itself, Gurdjieff and a small band of dedicated pupils, including Thomas and Olga de Hartmann, made perilous journeys to the Crimea and Tiflis. There they were joined by Alexandre and Jeanne de Salzmann, the former a well-known artist and theatrical designer and the latter a teacher of the Dalcroze system of rhythmic dance who was later to emerge as the principal guide under whom his teaching continued to be passed on after his death in 1949. It was in Tiflis, in 1919, that Gurdjieff created the first version of this Institute for the Harmonious Development of Man.
The account by Ouspensky and notes by other pupils published in 1973 under the title Views from the Real World show that in the Moscow period, before the journey out of Russia, Gurdjieff tirelessly articulated a vast body of ideas about man and the cosmos. It is appropriate here to interrupt the historical narrative in order to summarize these formulations, which played an important role in the subsequent development of his teaching, even as Gurdjieff changed the outer forms and certain inner emphases in his direct work with pupils. Also, to a limited extent, these ideas throw light on developments that came later, some of which have given rise to unnecessary confusion in the minds of outside observers. One caveat, however, is necessary. If in his writings Gurdjieff never sought merely to spread out a philosophical system, all the more in his direct work with pupils did he mercilessly resist the role of guru, preacher, or schoolteacher. In Search of the Miraculous shows, with considerable force, that Gurdjieff always gave his ideas to his pupils under conditions designed to break through the crust of emotional and intellectual associations which, he taught, shut out the small voice of conscience in man. The exquisite and often awesome precision with which he was able to break through that crust—ways of behaving with his pupils that were, in turn, shocking, mysterious, frightening, magical, delicately gentle, and omniscient—remains one of the principal factors around which both the Gurdjieff legend and the misunderstandings about him have arisen, as well as being the element most written about by those who came in touch with him and most imitated in the current age of “new religions.”
The Gurdjieff Ideas
It is true enough to say that Gurdjieff’s system of ideas is complex and all-encompassing, but one must immediately add that their formulation is designed to point man toward a central and simple power of apprehension which Gurdjieff taught is merely latent within the human mind and which is the only power by which man can actually understand himself in relation to the universe. In this sense, the distinction between doctrine and method, which is fairly clear in most of the older spiritual traditions, does not yet entirely obtain in the Gurdjieff teaching. The formulations of the ideas are themselves meant to have a special action on the sense of self and may therefore be regarded as part of the practical method. This characteristic of the Gurdjieff teaching reflects what Gurdjieff perceived as the center of gravity of modern man’s subjectivity—the fact that modern civilization is lopsidedly oriented around the thinking function. Modern man’s illusory feeling of “I” is built up around his thoughts and therefore, in accordance with the level of the pupil, the ideas themselves are meant to affect this false sense of self. For Gurdjieff the deeply penetrating influence of scientific thought in modern life was not something merely to be deplored, but to be understood as the channel through which the eternal Truth must first find its way toward the human heart.
Man, Gurdjieff taught, is an undeveloped creation. He is not really man, considered as a cosmically unique being whose intelligence and power of action mirror the energies of the source of life itself. On the contrary, man as we encounter him is an automaton. His thoughts, feelings, and deeds are little more than mechanical reactions to external and internal stimuli. He cannot do anything. In and around him, everything happens without the participation of his own authentic consciousness. But human beings are ignorant of this state of affairs because of the pervasive influence of culture and education, which engrave in them the illusion of autonomous conscious selves. In short, man is asleep. There is no authentic I am in his presence, but only an egoism which masquerades as the authentic self, and whose machinations poorly imitate the normal human functions of thought, feeling, and will.
Many factors reinforce this sleep. Each of the reactions that proceed in one’s presence is accompanied by a deceptive sense of I—man is many I’s, each imagining itself to be the whole, and each buffered off from awareness of the others. Each of these many I’s represents a process whereby the subtle energy of consciousness is absorbed and degraded, a process that Gurdjieff termed “identification.” Man identifies—that is, squanders his conscious energy, with every passing thought, impulse, and sensation. This state of affairs takes the form of a continuous self-deception and a continuous procession of egoistic emotions, such as anger, self-pity, sentimentality, and fear which are of such a pervasively painful nature that man is constantly driven to ameliorate this condition through the endless pursuit of social recognition, sensory pleasure, or the vague and unrealizable goal of “happiness.”
According to Gurdjieff, the human condition cannot be understood apart from considering humanity within the function of organic life on earth. The human being is constructed to transform energies of a specific nature, and neither his potential inner development nor his present actual predicament is understandable apart from this function. Thus, in the teaching of Gurdjieff, psychology is inextricably connected with cosmology and metaphysics and even, in a certain sense, biology. The diagram known as “the Ray of Creation” provides one of the conceptual keys to approaching this interconnection between humanity and the universal order, and as such invites repeated study from a variety of angles and stages of understanding.
In this diagram, the fundamental data about the universe gathered by science, and specifically the principal cosmic entities that modern astronomical observation has marked out, are arranged in a manner coherent with ancient metaphysical principles about humanity’s actual place in the scheme of creation. The reader is referred to chapters 5, 7, and 9 in In Search of the Miraculous for an explanation of this diagram, but the point to be emphasized here is that, at the deepest level, the human mind and heart are enmeshed in a concatenation of causal influences of enormous scale and design. A study of the Ray of Creation makes it clear that the aspects of human nature through which one typically attempts to improve one’s lot are without any force whatever within the network of universal influences that act upon man on earth. In this consists man’s fundamental illusion, an illusion only intensified by the technological achievements of modern science. Man is simply unable to draw upon the conscious energies passing through him, which in the cosmic scheme, are those possessing the actual power of causal efficacy. Man does not and cannot participate consciously in the great universal order, but instead is tossed about en masse for purposes limited to the functions of organic life on earth as a whole. Even in this relatively limited sphere—limited, that is, when compared to man’s latent destiny—mankind has become progressively incapable of fulfilling its function, a point that Gurdjieff strongly emphasized in his own writings. This aspect of the Ray of Creation—namely, that the “fate of the earth” is somehow bound up with the possibility of the inner evolution of individual men and women—resonates with the contemporary sense of impending planetary disasters.

“The Ray of Creation” in the teaching of Gurdjieff: The Absolute is the fundamental source of all creation. From the Absolute the process of cosmic creation branches and descends (involves) according to an ordered sequence of increasing complexity and density, following the law of the octave. The universe as a whole comprises countless such branchings from the Absolute; this particular diagram represents the “ray” containing our planet earth.
How are human beings to change this state of affairs and begin drawing on the universal conscious energies which they are built to absorb but which now pass through them untransformed? How is humanity to assume its proper place in the great chain of being? Gurdjieff’s answer to these questions actually circumscribes the central purpose of his teaching—namely, that human life on earth may now stand at a major transitional point comparable perhaps to the fall of the great civilizations of the past and that development of the whole being of man (rather than one or another of the separate human functions) is the only thing that can permit man to pass through this transition in a manner worthy of human destiny.
But whereas the descent of humanity takes place en masse, ascent or evolution is possible only within the individual. In Search of the Miraculous presents a series of diagrams dealing with the same energies and laws as the Ray of Creation, not only as a cosmic ladder of descent but also in their evolutionary aspect within the individual. In these diagrams, known collectively as the Food Diagram, Ouspensky explains in some detail how Gurdjieff regarded the energy transactions within the individual human organism. As in the Ray of Creation, the Food Diagram arranges the data of modern science, in this case the science of physiology, in a manner that subsumes these data naturally within the immensely vast scale of ancient metaphysical and cosmological principles. Again, the reader is referred to Ouspensky’s book, the point being that humanity can begin to occupy its proper place within the chain of being only through an inner work with the specific intrapsychic energies that correspond to the higher energies in the cosmic order and which within the individual human being may be subsumed under the general term attention. The many levels of attention possible for man, up to and including an attention that in traditional teachings has been termed Spirit, are here ranged along a dynamic, vertical continuum that reaches from the level of biological sustenance which humans require for their physical bodies up to the incomparably finer sustenance that they require for the inner growth of the soul. This finer substance is termed “the food of impressions,” a deceptively matter-of-fact phrase that eventually defines man’s unique cosmic obligation and potentiality of constantly and in everything working for the development within himself of the divine attributes of devotion to the Good and objective understanding of the Real.
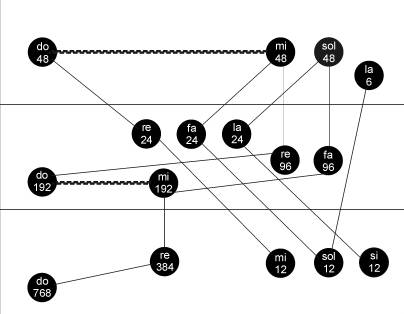
“The Food Diagram” in the teaching of Gurdjieff: the culmination of a series of diagrams illustrating the manner in which different qualities of energy are assimilated and evolve (following the law of the octave) in the human organism. This diagram represents the energy transactions in a moment of authentic consciousness.
The Ray of Creation and the Food Diagram, extraordinary though they are, are only a small part of the body of ideas contained in In Search of the Miraculous. They are cited here as examples of how Gurdjieff not only restated the ancient, perennial teachings in a language adapted to the modern mind but also brought to these ancient principles something of such colossal originality that those who followed him detected in his teaching the signs of what in Western terminology may be designated a new revelation.
However, as was indicated above, the organic interconnection of the ideas in In Search of the Miraculous is communicated not principally through conceptual argument but as a gradual unfolding which Ouspensky experienced to the extent that there arose within him that agency of inner unity which Gurdjieff called “the real I,” the activation of which required of Ouspensky a rigorous and ego-shattering inner work under the guidance of Gurdjieff and the group conditions he created for his pupils. Each of the great ideas in the book leads to the others. The Ray of Creation and the Food Diagram are inseparable from Gurdjieff’s teaching about the fundamental law of three forces and the law of the sevenfold development of energy (the Law of Octaves), and the interrelation of these laws as expressed in the symbol of the enneagram. The reflection of these ideas in man is inseparable from Gurdjieff’s teaching about the tripartite division of human nature, the three “centers” of mind, feeling, and body, and the astonishing account of how Gurdjieff structured the conditions of group work is inseparable from the idea of his work as a manifestation of the Fourth Way, a spiritual path distinct from the traditionally familiar paths termed “the way of the fakir,” “the way of the monk,” and “the way of the yogi.”
The notion of the Fourth Way is one of the Gurdjieff ideas that have captured the imagination of contemporary people and have brought quite a new meaning to the idea of esotericism itself. The meaning of this idea is perhaps best approached by resuming the narrative of Gurdjieff’s life, with special attention given to the conditions of work which he created for his pupils.
Gurdjieff’s own written statement of his teaching will be discussed below. But first it should be reemphasized that the diagnosis of the human condition which Gurdjieff brought and the means for human regeneration revolve around the quality and level of man’s being. This central aspect of Gurdjieff’s mission and his person seems to beggar description in words. The cosmological ideas are only one indication that what is at issue is a level of consciousness and energy within man and the universe that is unknown to modern psychology. There exists a particular Gurdjieffian “atmosphere” in his own writings, and in most accounts of his work with pupils, which evokes in some readers the same overall feeling and intellectual intuition that accompanies those unique experiences in life when the whole sense of oneself, including one’s familiar religious sense and sense of mystery, breaks down and when for a moment an unnamable emptiness and silence are experienced. The Gurdjieff teaching may perhaps be understood as a journey into and beyond that silence along with and by means of the demand to attend to the ordinary life of ourselves as we are. In any case, this central aspect of his teaching explains in part why at a certain level no comparisons of his teaching with traditional spiritualities are possible, while at deeper levels his ideas are being claimed by some activist followers of all the traditions and denied by others as spiritually invalid. The point is that this special “atmosphere” represents and manifests being and calls to that in a person which yearns for “something” that does not seem possible for one to find under most “known” forms of religion, science, psychology, and occultism.
After a brief period in Constantinople, Gurdjieff and his group of pupils made their way through Europe and finally settled in France where, in 1922, he established his Institute for the Harmonious Development of Man at the Chateau du Prieuré at Fontainebleau near Avon, just outside Paris. The brief, intense period of activity at the Prieuré has been described in numerous books, but even for those familiar with these accounts, the establishment and day-to-day activities of the Prieuré still evoke astonishment. It was during this period that Gurdjieff developed many of the methods and practices of group work that have retained a central place in the work of Gurdjieff pupils throughout the world today, including many of the movements or sacred dances that he reconstituted on the basis of his initiatic experience in monasteries and schools of awakening in Asia and the Levant. All serious accounts of the conditions Gurdjieff created at the Prieuré give the impression of a community life pulsating with the uncompromising search for truth engaging all sides of human nature—demanding physical work, intensive emotional interactions, and the study of a vast range of ideas about humanity and the universal world. These accounts invariably speak of the encounter with oneself that these conditions made possible and the experience of the self which accompanied this encounter.
The Prieuré attracted numerous artists and literary figures from America and England, many of whom were sent by P. D. Ouspensky who by that time had broken with Gurdjieff and was leading his own groups in London. Concerning his break with Gurdjieff, which is described with forceful compactness in In Search of the Miraculous, and pending a survey discussion below of Gurdjieff’s leading pupils, there are many indications that at the deepest personal level Ouspensky maintained a spiritual connection with Gurdjieff. But as one close observer has remarked,
As early as 1918 … Ouspensky began to feel that a break with Gurdjieff was inevitable, that “he had to go”—to seek another teacher or to work independently. The break between the two men, teacher and pupil, each of whom received much from the other, has never been satisfactorily explained. They met for the last time in Paris in 1930.2
The rationale that lay behind the conditions Gurdjieff created for his pupils, that is to say, the idea of the Fourth Way, can perhaps be characterized by citing the descriptive brochure published at the Prieuré in 1922:
The civilization of our time, with its unlimited means for extending its influence, has wrenched man from the normal conditions in which he should be living. It is true that civilization has opened up for man new paths in the domain of knowledge, science and economic life, and thereby enlarged his world perception. But, instead of raising him to a higher all-round level of development, civilization has developed only certain sides of his nature to the detriment of other faculties, some of which it has destroyed altogether.…
… modern man’s world perception and his own mode of living are not the conscious expression of his being taken as a complete whole. Quite on the contrary, they are only the unconscious manifestation of one or another part of him.
From this point of view our psychic life, both as regards our world perception and our expression of it, fails to present an unique and indivisible whole, that is to say a whole acting both as a common repository of all our perceptions and as the source of all our expressions. On the contrary, it is divided into three separate entities, which have nothing to do with one another, but are distinct both as regards their functions and their constituent substances.
These three entirely separate sources of the intellectual, emotional and instinctive or moving life of man, each taken in the sense of the whole set of functions proper to them, are called by the system under notice the thinking, the emotional and the moving centers.3
It is difficult conceptually, and in a few words, to communicate the meaning of this idea of the three centers, which is so central to the Gurdjieffian path. The modern person simply has no conception of how self-deceptive a life can be that is lived in only one part of oneself. The head, the emotions, and the body each have their own perceptions and actions, and each in itself, can live a simulacrum of human life. In the modern era this has gone to an extreme point and most of the technical and material progress of our culture serves to push the individual further into only one of the centers—one third, as it were, of one’s real self-nature. The growth of vast areas of scientific knowledge is, according to Gurdjieff, outweighed by the diminution of the conscious space and time within which one lives and experiences oneself. With an ever-diminishing “I,” man gathers an ever-expanding corpus of information about the universe. But to be human—to be a whole self possessed of moral power, will, and intelligence—requires all the centers, and more. This more is communicated above all in Gurdjieff’s own writings in which the levels of spiritual development possible for man are connected with a breathtaking vision of the levels of possible service that the developing individual is called on to render to mankind and to the universal source of creation itself.
Thus, the proper relationship of the three centers of cognition in the human being is a necessary precondition for the reception and realization of what in the religions of the world has been variously termed the Holy Spirit, Atman, and the Buddha nature.
The conditions Gurdjieff created for his pupils cannot be understood apart from this fact. “I wished to create around myself,” Gurdjieff wrote, “conditions in which a man would be continuously reminded of the sense and aim of his existence by an unavoidable friction between his conscience and the automatic manifestations of his nature.”4 Deeply buried though it is, the awakened conscience is the something more which, according to Gurdjieff, is the only force in modern man’s nearly completely degenerate psyche that can actually bring parts of his nature together and open him to that energy and unnamable awareness of which all the religions have always spoken as the gift that descends from above, but which in the conditions of modern life is almost impossible to receive.
The most active period of the Prieuré lasted less than two years, ending with Gurdjieff’s nearly fatal motor accident on July 6, 1924. In order to situate this period properly, it is necessary to look back once again to the year 1909 when Gurdjieff had finished his twenty-one years of traveling throughout Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Europe meeting individuals and visiting communities who possessed knowledge unsuspected by most people. By 1909 Gurdjieff had learned secrets of the human psyche and of the universe that he knew to be necessary for the future welfare of humanity, and he set himself the task of transmitting them to those who could use them rightly. After trying to cooperate with existing societies, he decided to create an organization of his own. He started in 1911 in Tashkent, where he had established a reputation as a wonder-worker and an authority on “questions of the Beyond.” He moved to Moscow in 1913 and after the revolution of February 1917 there began his astonishing journeys through the war-torn Caucasus region, principally Essentuki and Tiflis, leading a band of his pupils to Constantinople and finally to France, where he reopened his institute at the Chateau de Prieuré at Avon. His avowed aim during this period was to set up a worldwide organization for the dissemination of his ideas and the training of helpers. The motor accident of July 1924 occurred at this critical juncture.
When he began to recover from his injuries, Gurdjieff was faced with the sheer impossibility of realizing his plans for the institute. His health was shattered; he had no money; and many of his friends and pupils had abandoned him. He was a stranger in Europe, neither speaking its languages nor understanding its ways. He made the decision to find a new way of transmitting to posterity what he had learned about humanity, human nature, and human destiny. This was to be done by writing. His period as an author began in December of 1924 and continued until, in May 1935, he stopped writing and changed all his plans.
Gurdjieff’s Writings
While he was still recuperating from his injuries, Gurdjieff began his work as a writer, dictating to his secretary Olga de Hartmann the opening lines of his most important book, Beelzebub’s Tales to His Grandson. His two later books, Meetings with Remarkable Men and the unfinished Life is Real Only Then When ‘I Am,’ have major aspects about them that are accessible only to pupils of the teaching—this is overwhelmingly true of the latter. But Beelzebub was written for the world.
It is an immense and unique work in every sense of the term. Cast as an allegory, it is the narrative of the once fiery rebel Beelzebub, who for his youthful indiscretion spent long years in our solar system, where, among his other activities, he had occasion to study that very minor planet Earth and its inhabitants. In these tales to his young grandson, Beelzebub comes back constantly to the causes of man’s alienation from the sources of his own life and, at the same time, points in the direction toward which man could consciously evolve. Touching on one after another of the myriad aspects of human history from its earliest beginnings to modern times, Beelzebub continually brings his perceptions back to the same cosmic laws that govern both the working of nature and the psychic life of humans and, in so doing, bodies forth the picture of a living and conscious universe. In this universe, humanity, falling further away from an understanding of its source and the place it can occupy, has forgotten its function and lost all sense of its direction.
Beelzebub traces this failure with compassion and often with superb humor. His tenderness toward the undeveloped possibility represented by his grandson strikes the underlying note of the book, which is one of deep concern for the fulfillment of the individual human life.
This bare summary can give no impression of the extraordinary nature of this book. Intentionally written in complex, intricate style and making frequent use of strange-sounding neologisms, the book gradually yields its meanings only after repeated readings. Each reading of it opens new facets of Gurdjieff’s teaching, not only in intellectual terms but at deep, subconscious levels.
Gurdjieff’s Influence
During the writing of Beelzebub’s Tales, Gurdjieff continued to live and receive pupils at the Prieuré and remained based there until 1933. During this period—between 1924 and 1933—A. R. Orage had gone to America, where he attracted a number of serious pupils, and where he made known the Gurdjieff teaching to some of America’s leading artists and writers. At the same time, Ouspensky was in London lecturing and working to form his own school (it was through Ouspensky that Orage had first come into contact with the Gurdjieff teaching). Among the other well-known figures who studied under Ouspensky were Maurice Nicoll, Kenneth Walker, and P. L. Travers. Nicoll later went on to lead his own groups and write several influential books that reflected his work with the Gurdjieff ideas: The New Man, a pioneering study of the parables of Christ, and Living Time, which developed Ouspensky’s theories about the dimensions of space and time.
In France, during the 1920s, Gurdjieff’s institute had already suffered some notoriety when he accepted the dying Katherine Mansfield into the community of the Prieuré. Although Gurdjieff shunned publicity, a number of press accounts of life at the Prieuré, some foolish and slanderous, appeared in France and England in the early 1920s. After the automobile accident, however, and the consequent closing down of the intensive activities of the institute, Gurdjieff’s work as a teacher attracted less public attention. In the late 1920s and early 1930s several other well-known writers became pupils, notably René Daumal, Margaret Anderson, and Kathryn Hulme. Daumal’s writings, especially his unfinished masterpiece, Mount Analogue, are among the most vital and reliable literary expressions of certain key aspects of the Gurdjieff teaching.
In 1932 Gurdjieff left the Prieuré and settled in Paris, which was to remain his base until his death in 1949. By 1933, Orage had separated from Gurdjieff after some years of working with groups in America. He died in England in 1934. The work of Ouspensky, however, went on in London and then later also in New York. Ouspensky’s book Tertium Organum had been published with considerable success in England in the early 1920s and had established his reputation as a writer about metaphysical subjects. This book, much of it written before he had met Gurdjieff, maintained its popularity throughout the 1930s and 1940s and deserves special consideration, both as an important philosophical work in its own right and as a clue to the nature of Gurdjieff’s influence upon those who became his close pupils.
Writing in the early part of the twentieth century, long before experiments with altered states of consciousness became a widespread aspect of the “new religions” movement, Ouspensky was seriously experimenting with altered states of consciousness and their effect on perception and cognition. His own experiences brought him to the conclusion that new forms and categories of thought were needed, quite apart from the two modes of thought (classical and positivistic) that had dominated Western civilization for over two thousand years. Tertium Organum is the fruit of these experiments. The book is dominated by the idea of higher dimensions, “eternal recurrence,” and the insight that higher forms of knowledge must inevitably be associated with the development of the capacity for feeling—that is to say, the perception of truth is inseparable from the development of inner moral power. These basic ideas are developed in full in the book and, in one form or another, have entered as an influence into the writings of many modern philosophers and writers both in the West and in Russia. What distinguishes this book is not only the force of Ouspensky’s vision but the fact that it was rooted in his own experience, rather than solely from reflecting on traditional ideas. Thus Ouspensky may be considered a modern pioneer in what can be called “inner empiricism,” a mode of philosophizing about the kind of metaphysical issues which scientific thought has largely dismissed, but which retains the scientific attitude that seeks to base all theory on actual experience and carefully conducted experiments. Ouspensky’s inner world was his own metaphysical laboratory.
Of particular significance here, however, is the fact that the book, written before Ouspensky became a pupil of Gurdjieff, contains numerous ideas and formulations which later appear intact in Ouspensky’s account in In Search of the Miraculous as elements of the Gurdjieff teaching. This raises the question of the kind of help that Gurdjieff offered to those who followed him and shows the exceptional degree to which Ouspensky was prepared for such a teaching. In Ouspensky’s case, there is no doubt that he opened himself to the vast body of new ideas which Gurdjieff brought forth. But it is also clear that, at the same time, he retained a great deal of his own previously acquired understanding of the human situation and the universal order. Somehow, under Gurdjieff, the questions that Ouspensky had wrestled with and the new ideas he had come to were now situated in a broader and more balanced perspective, taking on subtle new shadings that made them, in his mind, far more precise and integrated within an immensely more comprehensive worldview. When compared with Tertium Organum, In Search of the Miraculous does not, therefore, represent a rupture in Ouspensky’s thinking so much as an extraordinary flowering of it, whereby it became, so to say, an instrument serving a new aim and the vehicle for another quality of energy. He began as an imposing thinker, and after Gurdjieff he remained a powerful thinker who has also become a different kind of man. Comparable observations are germane as well in the case of the composer Thomas de Hartmann, the quality of whose musical talent underwent an astonishing transformation under Gurdjieff.
These observations may be of help to anyone trying to assess the extent and nature of Gurdjieff’s influence, both on those who worked with him and on those who have come after him, as well as his place in spiritual currents of modern civilization. Much grief is in store for investigators who try to trace Gurdjieff’s influence on the culture under more conventional rubrics. It is true that a growing number of people now espouse what might be called a Gurdjieffian philosophy or psychology, but to focus on this aspect of his influence is to miss the essential aspect of his work and the only true standard by which his impact on our culture can really be measured. Like the founders of every great spiritual path, he sought to awaken rather than to indoctrinate. The course of his life as teacher does not follow the logic of an individual seeking merely to spread a doctrine.
When therefore, it is admitted that Gurdjieff’s influence has affected a great many fields and disciplines—such as religion, literature, psychology, philosophy, the visual arts, music, dance, etc.—it must be added that this influence does not represent a fanatical adherence to “Gurdjieffian” standards or ideals which are alien to the field at hand. The influence of Gurdjieff would show itself, rather, in certain underlying values and concerns—that is to say, in a deeper understanding of the work at hand rather than an eccentric understanding.
How, then, to regard the most externally visible ways in which his ideas and formulations have entered into modern culture? It can be argued, for example, that the word “consciousness” acquired the spiritual connotations which it now has because of Gurdjieff’s use of the term to designate an aspect of the mind higher than ordinary thought. Or, as mentioned above, it is clear that his notion of the Fourth Way, that is, a rigorous spiritual discipline conducted in the midst of an individual’s ordinary life activities, has been adopted by numerous religious and psychoreligious groups throughout the West. His emphasis on the role of self-observation has also had widespread influence, to the extent that there is a vague, but common, understanding among spiritual seekers today that the alternatives of introspection or positivistic behaviorism by no means exhaust the possibilities of one’s ability to study and know oneself. In addition, modern concepts of group dynamics were strongly influenced by what he brought; indeed, the whole idea of the need for group work in order to affect psychological or behavioral change of any kind may be traced, in part, to Gurdjieff’s emphasis on the group, rather than the Oriental guru-disciple relationship, as indispensable to Western spiritual development. But just as Gurdjieff’s influence cannot be measured by the number of individuals who espouse his ideas, neither can his influence on the culture be measured by verbal formulations or concepts which he originated and which enjoy a certain fashion. Either Gurdjieff helped to create authentic men and women or he did not. The extent to which he did so is the extent to which his influence is to be valued.
Gurdjieff’s School
Having opened the question of how to regard the influence of Gurdjieff, it is now possible to speak briefly about the chief means by which his influence may become a factor in our civilization. Obviously the term “school,” when applied to the Gurdjieff teaching, does not and cannot refer only to a loosely connected group of followers sharing intellectual beliefs or attitudes. The term has a very precise meaning in the Gurdjieff teaching, somewhat akin to the meaning of “monastery,” “ashram,” or “brotherhood” as they are used in the history of religious tradition, or as they are applied, say, to the school of Pythagoras or the schools of the medieval and Renaissance painters. It is through a group of individuals studying and working together at varying levels that the transmission of his teaching was intended to take place. As has already been noted, it is clear that he did not believe Western man could be spiritually helped past a certain point by the traditional Eastern forms of relationship between a guru and an individual pupil. At the same time, he strongly emphasized that guidance was indispensable and that no one individual could hope to attain liberation working alone. A “school,” considered to be a dynamic ordering of precise moral, psychological, and physical conditions within which a relatively small number of individuals can interact for the sake of self-development, became the principal form of transmission. Only such conditions, Gurdjieff taught, could allow older, more experienced pupils to pass on their understanding as part of their own inner work, while enabling all parties to take into account the ever-present tendencies to inattention, suggestibility, and fantasy. The Gurdjieff “school” thus represents an attempt to establish a school of awakening specifically adapted to modern life—with all the tension and paradox that phrase suggests when taken within the overwhelmingly materialistic context of modern civilization, that is, its overwhelming and omnipresent tendency to draw men and women out of themselves toward externals, instead of calling them back to the sources of the spirit.
Although a number of well-known individuals have been and are associated with the Gurdjieff Work, as the school is called following the meaning of the word in the alchemical tradition, many of Gurdjieff’s leading pupils have chosen to remain unknown to the public, as have many of the leaders who represent the second and third generation of the teaching. Attempts to portray the nature of the membership by citing only those figures known to the public can therefore be misleading. As a general rule, those engaged in the Work pursue their ordinary lives without calling attention to their affiliation.
The Gurdjieff Foundation
After Gurdjieff’s death in Paris in 1949, his work was carried on by his closest pupil and collaborator, Jeanne de Salzmann, under whose guidance centers of study were gradually established in Paris, New York, London, and Caracas. Over the past fifty years other centers of work have radiated from them in major cities of the Western world. The pupils living in America established the Gurdjieff Foundation of New York in 1953. Shortly thereafter, groups were started on the West Coast and in Canada. Similar branches of varying size have been formed throughout the world and at present there may be between five and ten thousand persons in the Americas, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Middle East studying this teaching under the guidance of pupils who worked personally with Gurdjieff when he was alive. The main centers of study remain Paris, New York, and London because of the relatively large concentration of first-generation Gurdjieff pupils in these cities. Most of the groups maintain close correspondence with the principal centers, usually in relationship to one or two of the pupils who often travel to specific cities in order to guide the work of these groups. The general articulation of these various groups, both within America and throughout the world, is a cooperative one, rather than one based on strictly sanctioned jurisdictional control. There are also groups who no longer maintain close correspondence and operate independently.
The Gurdjieff Foundation offers its students a variety of activities whose form and emphasis change to some extent in response to cultural conditions and individual needs. Usually, inquiries and experiments are conducted in small groups under conditions that have the potential for developing in each individual the faculty of attention. As has already been indicated, the Gurdjieff teaching offers a remarkably comprehensive psychology of levels of attention and a many-sided practical method for developing access to this power in relationship to the three basic sources of perception in the human psyche—the three centers.
From the outset, pupils are encouraged and assisted in the study of the liberation of attention, which remains unexplored in the conditions of modern life. Such work is understood to be indispensable for what Gurdjieff called “self-observation.” In fact, as has also been indicated, Gurdjieff taught that this is a universal and essential discipline, which was conveyed by Socrates and ancient teachings in the words of the Delphic oracle—“Know thyself”—as well as in the Gospels under the cryptic one-word command gregoreite (awake) and in Buddhism under the designation nana dhasana (vision). But although clear enough to initiates in these ancient traditions, it is practically inaccessible to a modern Western-educated individual. The many and various forms of work offered by the Gurdjieff Foundation are understood as a way for modern people to grasp and put into practical use this discipline which is said to be literally indispensable to real progress in the regenerate life.
The Gurdjieff Foundation approaches the question of obedience and authority, which is of such concern in the modern world, in this context. By voluntarily subjecting oneself to such a work of self-study, the student may come to realize that not only is one responsible for one’s own work, and that on one level the student can and must rely only on himself or herself, but also that on a larger scale the student is entirely dependent on the help of others similarly engaged. Thus, in essence and in actual practice, nothing is given to a student unless the student asks for it, and then only after the student has studied the theory of the teaching sufficiently to understand intellectually the nature of the help being asked for.
Related to this orientation is the basic Gurdjieff idea of a “Way in Life,” which, as has been mentioned, has exerted considerable influence, under varying interpretations, on many new religious and psychological movements in the Western world. As practiced by the Foundation, it means that the student seeks to understand life as it is, without attempting to alter anything in the name of inner development. Relationships to family, vocation, personal ties, and obligations are, at least to start with, left intact both for the material they provide for self-understanding and for the ultimate value and force that all human relationships contain when they are engaged in with a more central and harmonious attention.
The activities of the Foundation include the study of the Gurdjieff ideas, group meetings, study of the movements and sacred dances left by Gurdjieff, music, crafts and household work, the study of traditions, public demonstrations of work, and work with children and young people.
In group meetings students verify the authenticity of their observations through expressing them in the presence of others. The place of group leader is taken by one or several experienced pupils, and great care is taken that these meetings do not revolve around the person of the leader or turn into speculative, psychological discussions or encounters. These meetings have little in common with either group therapy sessions or with religious / spiritual meetings in their known forms.
Crafts and household work are engaged in principally as a means of throwing light on the details of everyday life and to expose the cumulative force of self-illusion and passivity that holds sway even in the most “favorable” stations of life.
Gurdjieff reconstituted the “movements” exercises he had met with in Central Asia for his own pupils under intensive conditions of inner discipline. Through the guidance of Jeanne de Salzmann (1889–1990) and Jessmin Howarth (1892–1984), the Foundation has taken precautions to transmit these exercises under comparable conditions as part of the central aim of developing the moral and spiritual power of individuals through the study and growth of the attention factor in the human organism. It is assumed that without the help of prepared teachers and without a solid connection to the ideas and the inner work, the practice of the movements cannot give the results intended. Therefore, at present, the movements are studied mainly at the principal established centers. Under Jeanne de Salzmann, a series of films documenting the movements has been made in order to preserve a record of the quality of inner work that the movements demand.
Group meetings and, where they are taught, the movements are comparatively invariant forms of practice of the Gurdjieff Foundation. The numerous other forms show more variety from center to center, depending on the makeup of the group and the specific line of inquiry that is held to be most useful at a given time or place.
The membership of the Gurdjieff Foundation worldwide exhibits considerable diversity with respect to social class, age, occupation, and educational background, although exact statistics are unavailable. Like Gurdjieff himself during his life, the Foundation attracts the interest of a surprisingly wide variety of people.
Notes
- Review of the film Meetings with Remarkable Men, in Material for Thought, San Francisco: Far West Editions, Spring 1980, No. 8, p. 86.
- John Pentland, entry on P. D. Ouspensky in The Encyclopedia of Religion, New York: Macmillan, 1987, Vol. 11, p. 143; Gurdjieff International Review, Vol. II (2), January 1999, pp. 5–6.
- G. Gurdjieff’s Institute for the Harmonious Development of Man: Prospectus No. 1, p. 3 (privately printed, 1922); Gurdjieff International Review, Vol. I (1), October 1997.
- G. I. Gurdjieff, Meetings with Remarkable Men, New York: Dutton, 1969, p. 270.
~ • ~
Jacob Needleman is Professor of Philosophy at San Francisco State University and the author of many influential books, including The New Religions (1970), The Heart of Philosophy (1982), Money and the Meaning of Life (1991, Rev. 1994), and Time and the Soul (1998). His most recent book is The American Soul (2003). This essay was previously published in Modern Esoteric Spirituality edited by Antoine Faivre and Jacob Needleman, New York: Crossroad, 1992. It is republished here with the kind permission of the author.Copyright © 1992, 1999 Jacob Needleman; revised May 24, 2002. This webpage © 2004 Gurdjieff Foundation of Washington